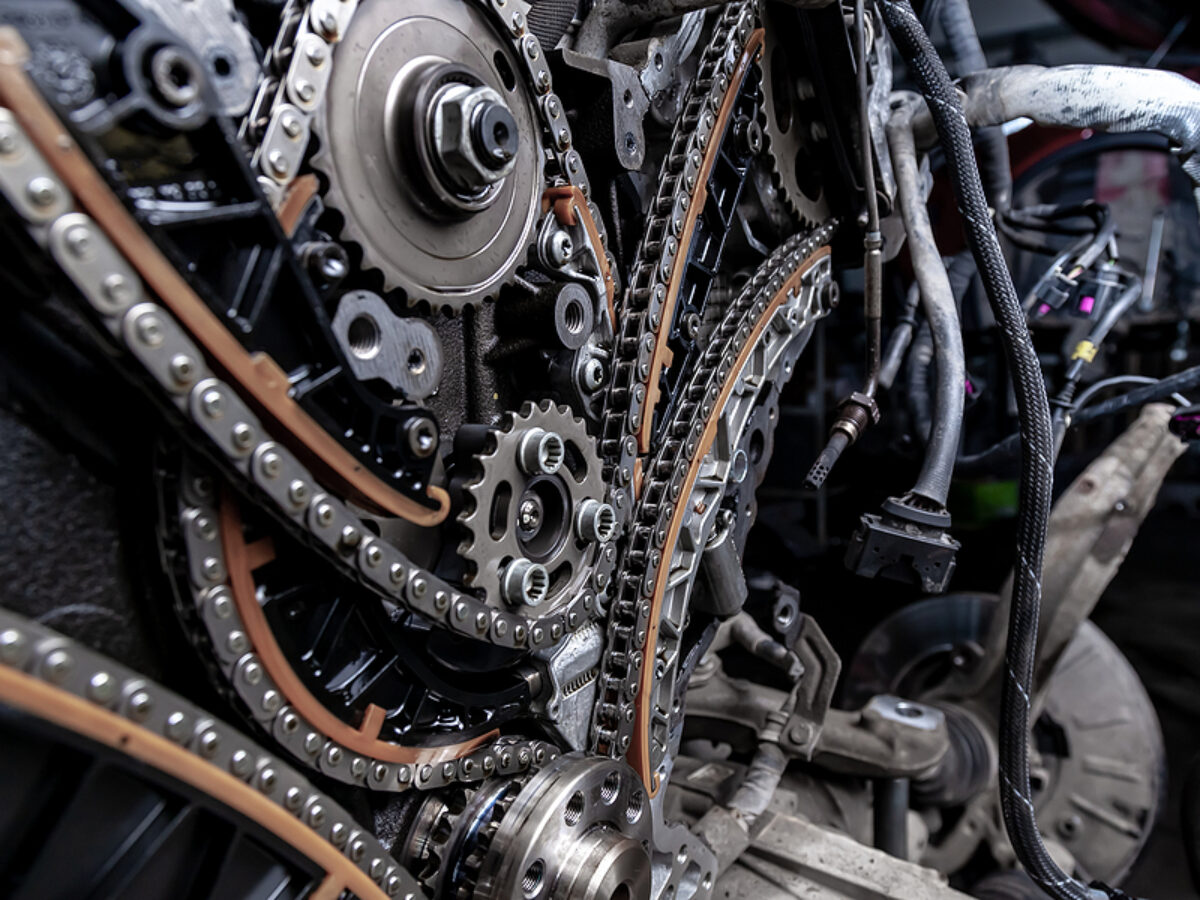
Ever wondered what keeps your car's engine ticking like a well-oiled clock? Chances are, it involves either a timing chain or a timing belt. These unsung heroes synchronize the crankshaft and camshaft, ensuring your engine's valves open and close at precisely the right moments. But what exactlyisthe difference between them? And which one is better for your vehicle?
Let's be honest, car maintenance can feel like navigating a minefield. Figuring out what's vital and what's not, understanding complex terminology, and knowing when to trust a mechanic can be overwhelming. Many drivers struggle with understanding the nuances of engine components, especially when it comes to essential parts like the timing system. Ignoring this crucial system can lead to expensive repairs and potential engine failure, which is something no one wants.
This guide dives deep into the key distinctions between timing chains and timing belts, shedding light on their pros, cons, maintenance needs, and overall impact on your vehicle's performance and longevity. By understanding these differences, you'll be better equipped to make informed decisions about your car's upkeep and avoid costly surprises down the road.
Essentially, timing chains are robust, metal-link systems designed for long-term durability, often lasting the lifespan of the engine. They are typically found in higher-performance vehicles or those prioritizing longevity. Timing belts, on the other hand, are made of reinforced rubber and offer quieter operation, but require periodic replacement. Key factors to consider are cost, maintenance intervals, noise levels, and the overall reliability desired. This is related to engine timing, car maintenance, auto repair, engine components, and vehicle longevity.
Understanding the Lifespan: Chain vs. Belt
I'll never forget the day my old pickup truck, bless its rusty soul, decided to stage a dramatic roadside breakdown. I was miles from anywhere, and the tow truck driver diagnosed the issue as a snapped timing belt. At that moment, I realized how crucial these little components are!
The key difference in lifespan is a major factor for many car owners. Timing chains are generally built to last the life of the engine. They are made from metal and are constantly lubricated by engine oil, which reduces wear and tear. Think of them like a bicycle chain, constantly moving and enduring pressure. Because of their robust design and constant lubrication, they rarely need replacement unless there's a specific problem with the engine itself.
Timing belts, in contrast, have a finite lifespan. Manufacturers typically recommend replacement intervals, often between 60,000 and 100,000 miles. These belts are made from rubber reinforced with cords, and they degrade over time due to heat, oil exposure, and constant flexing. Ignoring the recommended replacement interval can lead to a catastrophic engine failure if the belt snaps. While a timing belt replacement is cheaper than a chain replacement, the long-term cost can be higher due to the need for more frequent servicing.
Performance and Noise: Which is Quieter?
Timing belts are generally quieter than timing chains. The rubber construction of the belt absorbs vibrations and reduces noise. This can be a significant advantage in vehicles where noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH) are a concern, particularly in luxury cars or those designed for a smooth and comfortable ride.
Timing chains, being made of metal, tend to generate more noise. This noise can manifest as a subtle whirring or whining sound, which is often masked by other engine noises. However, in some cases, a worn or loose timing chain can produce a noticeable rattling sound.
From a performance standpoint, both timing chains and timing belts can accurately control valve timing. The choice often depends on the engine design and the manufacturer's preferences. Some high-performance engines use timing chains for their robustness and ability to withstand high RPMs and demanding conditions. Others may opt for timing belts to reduce weight and improve engine responsiveness. The performance difference between the two is often negligible in standard driving conditions, but in extreme performance scenarios, the superior strength of a timing chain can be beneficial.
The History and Evolution of Timing Systems
The history of timing systems in internal combustion engines is a fascinating journey. Early engines often used gears to directly link the crankshaft and camshaft. However, gears can be noisy and inefficient, leading to the development of timing chains and later timing belts.
Timing chains have been around for a long time, evolving from simple roller chains to more sophisticated designs with multiple rows of links for increased strength and durability. The introduction of hydraulic tensioners helped to maintain proper chain tension and reduce noise.
Timing belts gained popularity in the mid-20th century as advancements in rubber technology made them more reliable and durable. They offered a quieter and lighter alternative to timing chains. However, early timing belts were prone to failure, leading to a perception of unreliability that persists to some extent today.
Over time, timing belt technology has improved significantly, with the introduction of stronger materials and more advanced designs. Modern timing belts are much more reliable than their predecessors, but they still require periodic replacement. The choice between a timing chain and a timing belt often comes down to a balance of factors, including cost, noise, durability, and manufacturer preferences.
Hidden Secrets: Understanding the Tensioner
One of the often-overlooked components of a timing system is the tensioner. Whether you have a timing chain or a timing belt, the tensioner plays a critical role in maintaining proper tension and preventing slippage. Without a properly functioning tensioner, the timing can become inaccurate, leading to poor engine performance or even damage.
Timing chain tensioners are typically hydraulically operated, using engine oil pressure to maintain constant tension. They often incorporate a ratchet mechanism to prevent the tensioner from retracting when the engine is not running. Timing belt tensioners can be either spring-loaded or hydraulically operated. They are designed to automatically adjust for belt stretch and wear over time.
A failing tensioner can manifest in various ways, including unusual noises, such as rattling or squealing, and poor engine performance. In the case of a timing belt, a loose tensioner can cause the belt to skip teeth, leading to significant engine damage. Regularly inspecting and replacing the tensioner along with the timing chain or belt is essential for maintaining the health of your engine. Ignoring the tensioner can be a costly mistake, as it can lead to premature wear or failure of the entire timing system.
Recommendations: When to Replace and What to Look For
When it comes to timing chains and belts, proactive maintenance is key. For timing belts, adhere strictly to the manufacturer's recommended replacement interval. This interval is typically found in your vehicle's owner's manual and is based on mileage or time, whichever comes first.
For timing chains, there is generally no scheduled replacement interval. However, it's essential to be aware of the warning signs of a worn or failing chain. These signs can include a rattling noise from the engine, especially at startup, poor engine performance, and a check engine light. If you notice any of these symptoms, it's crucial to have your engine inspected by a qualified mechanic.
When replacing a timing belt or chain, it's always a good idea to replace the tensioner and any associated pulleys or guides. These components are often subject to the same wear and tear as the belt or chain and can contribute to premature failure if not replaced. Using high-quality replacement parts is also essential to ensure longevity and reliability.
The Role of Water Pump
Often, the water pump is driven by the timing belt. Because of this setup, many mechanics recommend replacing the water pump whenever the timing belt is replaced. This is because the labor cost to access the water pump is nearly the same as the labor cost to replace the timing belt. By replacing both at the same time, you save on potential future labor costs if the water pump were to fail shortly after the timing belt replacement.
A water pump failure can lead to overheating, which can cause severe engine damage. Therefore, replacing the water pump proactively can be a smart preventative measure. When replacing the water pump, be sure to use a high-quality replacement part from a reputable manufacturer. Some aftermarket water pumps may not meet the original equipment manufacturer's specifications, which can lead to premature failure.
Maintenance Tips for Timing Chains and Belts
While timing chains are generally low-maintenance, ensuring proper engine lubrication is crucial for their longevity. Regularly changing your engine oil and using the correct type of oil as specified by the manufacturer will help to keep the timing chain lubricated and reduce wear.
For timing belts, there's not much you can do to extend their lifespan beyond adhering to the recommended replacement interval. However, it's essential to keep the engine compartment clean and free of debris, as this can help prevent premature wear of the belt.
Also, avoid exposing the timing belt to oil or other contaminants, as this can cause it to deteriorate more quickly. If you notice any signs of oil leakage near the timing belt cover, it's essential to have it addressed promptly to prevent damage to the belt. Regular visual inspections can help you spot potential problems early on.
Inspect the Belt Regularly
For vehicles with timing belts, a visual inspection of the belt can sometimes reveal early signs of wear and tear. Look for cracks, fraying, or missing teeth. However, keep in mind that some damage may not be visible to the naked eye, so it's still crucial to adhere to the recommended replacement interval.
Also, pay attention to any unusual noises coming from the engine. A squealing or chirping sound could indicate a loose or worn belt. A rattling sound could indicate a problem with the tensioner or idler pulley. If you hear any unusual noises, it's best to have your engine inspected by a qualified mechanic.
If you are comfortable working on cars, you can inspect the timing belt yourself. However, be sure to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully and take all necessary safety precautions. If you're not comfortable performing the inspection yourself, it's best to leave it to a professional.
Fun Facts About Timing Systems
Did you know that some engines use a combination of timing chains and timing belts? These hybrid systems often use a timing chain to drive one camshaft and a timing belt to drive the other. This allows manufacturers to take advantage of the benefits of both systems, such as the durability of a timing chain and the quietness of a timing belt.
Also, some modern engines use variable valve timing (VVT) systems, which allow the engine to adjust the timing of the intake and exhaust valves based on engine speed and load. These systems can improve fuel efficiency, reduce emissions, and increase engine power. VVT systems can be used with both timing chains and timing belts.
Finally, the process of replacing a timing belt can be quite complex, especially on some engines. It often involves removing several other engine components, such as the water pump, crankshaft pulley, and engine mounts. It's essential to follow the manufacturer's instructions carefully and use the correct tools to avoid damaging the engine.
How to Choose Between a Chain and a Belt (If You Have a Choice)
Unfortunately, you don't usually get a choice between a timing chain and a timing belt. The type of timing system is determined by the engine design, and you can't typically convert from one to the other. However, if you're considering buying a new or used car, it's worth considering the type of timing system it has.
If you prioritize longevity and low maintenance, a timing chain is generally the better option. If you prioritize quietness and are willing to adhere to the recommended replacement interval, a timing belt can be a good choice. Also, consider the cost of replacement. While timing belt replacements are generally cheaper than timing chain replacements, the long-term cost can be higher due to the need for more frequent servicing.
Ultimately, the best choice depends on your individual needs and preferences. Consider your driving habits, budget, and maintenance preferences when making your decision.
What If the Timing Chain or Belt Breaks?
The consequences of a broken timing chain or belt can be severe, especially on interference engines. An interference engine is one where the valves and pistons can collide if the timing is off. If the timing belt or chain breaks on an interference engine, the valves can slam into the pistons, causing significant damage to the engine. This can result in bent valves, damaged pistons, and even a cracked cylinder head.
The cost of repairing a damaged interference engine can be quite high, often exceeding the value of the car. In some cases, it may be more cost-effective to replace the entire engine. Non-interference engines are more forgiving, as the valves and pistons will not collide if the timing is off. However, a broken timing belt or chain can still cause the engine to stall and require repairs.
To avoid the catastrophic consequences of a broken timing chain or belt, it's essential to adhere to the manufacturer's recommended replacement interval for timing belts and to be aware of the warning signs of a worn or failing timing chain.
Top 5 Differences Between Timing Chains and Belts
Here's a quick listicle to summarize the key differences:
1.Material: Timing chains are made of metal, while timing belts are made of reinforced rubber.
2.Lifespan: Timing chains typically last the life of the engine, while timing belts require periodic replacement.
3.Noise: Timing belts are generally quieter than timing chains.
4.Cost: Timing belt replacements are generally cheaper than timing chain replacements, but the long-term cost can be higher.
5.Maintenance: Timing chains require minimal maintenance, while timing belts require adherence to the recommended replacement interval.
Question and Answer
Q: How do I know if my car has a timing chain or a timing belt?
A: Check your owner's manual. It should specify the type of timing system your engine has and the recommended replacement interval for the timing belt (if applicable).
Q: What happens if I don't replace my timing belt on time?
A: The timing belt can break, potentially causing catastrophic engine damage, especially on interference engines.
Q: Can I replace a timing belt myself?
A: Replacing a timing belt can be a complex and time-consuming task. It's best left to a qualified mechanic, unless you have extensive automotive experience and the proper tools.
Q: Are timing chains really maintenance-free?
A: While timing chains are generally low-maintenance, they still require proper engine lubrication. Regular oil changes are essential for their longevity.
Conclusion of The Key Differences Between a Timing Chain and a Timing Belt
Hopefully, this guide has clarified the key differences between timing chains and timing belts. While both systems serve the same fundamental purpose, their design, maintenance requirements, and overall lifespan differ significantly. Understanding these differences will empower you to make informed decisions about your vehicle's maintenance and ensure its long-term reliability. Whether you're driving a car with a robust timing chain or a quiet timing belt, remember that proper maintenance is key to keeping your engine running smoothly for years to come. This discussion encompassed engine timing, car maintenance, auto repair, engine components, and vehicle longevity.