what is the origin of biomass energy
Top 20 Biomass Energy Pros and Cons
Biomass energy is a renewable source of energy derived from organic materials such as plants and animals. It has gained popularity as an alternative to fossil fuels due to its potential environmental benefits. In this article, we will explore the pros and cons of biomass energy.
Most Asked Questions about Biomass Energy
- Question 1: How does biomass energy work?
- Combustion and biochemical conversion are the two main methods of generating biomass energy.
- Combustion releases heat, which can be utilized to produce electricity or heat.
- Biochemical conversion involves the decomposition of biomass materials to produce biogas.
- Question 2: What are the advantages of biomass energy?
- Renewable: Biomass is derived from organic materials, which are constantly being replenished.
- Reduced carbon emissions: Biomass plants can be carbon neutral or even carbon negative if sustainable biomass sources are used.
- Diversification of energy sources: Biomass energy provides an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
- Utilization of waste materials: Biomass energy can be generated from agricultural waste, wood residues, or dedicated energy crops, reducing landfill waste.
- Question 3: What are the disadvantages of biomass energy?
- High emissions: Combustion of biomass releases carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which contribute to air pollution.
- Land and water requirements: Biomass crops can compete with food crops for land and water resources, leading to potential conflicts.
- Transportation and storage challenges: Biomass materials need to be transported and stored, which can be logistically challenging and costly.
- Inefficient energy conversion: Biomass energy conversion processes can have lower energy efficiency compared to traditional fossil fuel power plants.
- Question 4: Is biomass energy sustainable?
- Question 5: What are the different types of biomass sources?
- Wood and agricultural residues: These include forest residues, wood chips, sawdust, straw, and husks.
- Dedicated energy crops: Certain crops like switchgrass, miscanthus, and fast-growing trees can be grown specifically for energy production.
- Landfill gas: Biomethane is generated from the decomposition of organic waste in landfills.
- Algae: Algae biomass can be cultivated and harvested for energy production.
- Question 6: How is biomass energy different from other renewable energy sources?
- Question 7: Can biomass energy be used in transportation?
- Question 8: What is the potential for biomass energy in reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
- Question 9: Can biomass energy contribute to rural development?
- Question 10: Are there any government incentives or policies supporting biomass energy?
- Question 11: What are the challenges in scaling up biomass energy production?
- Feedstock availability: Ensuring a consistent and sufficient supply of biomass feedstocks can be challenging, especially in regions with limited agricultural or forestry resources.
- Technological limitations: Developing efficient and cost-effective biomass conversion technologies is crucial for large-scale deployment.
- Environmental concerns: Proper management of land use, water resources, and prevention of deforestation are important to ensure the environmental sustainability of biomass energy.
- Question 12: Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels entirely?
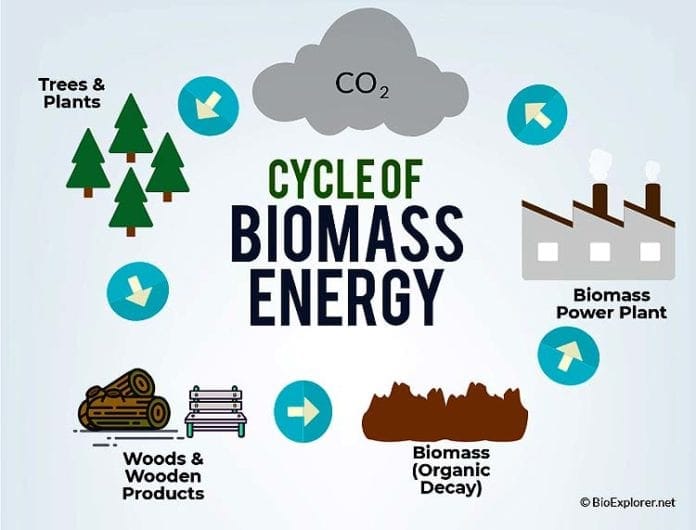
Answer: Biomass energy is generated through the process of combustion or biochemical conversion. In combustion, biomass materials such as wood, agricultural residues, or dedicated energy crops are burned to release heat, which is then used to generate electricity or produce heat. Biochemical conversion involves the decomposition of biomass materials through biological processes such as anaerobic digestion. This produces biogas, which can be used as a fuel or converted into electricity or heat.
Answer: Biomass energy offers several benefits:
Answer: Despite its benefits, biomass energy has some drawbacks:
Answer: The sustainability of biomass energy depends on the source and management of biomass materials. If sourced from sustainably managed forests or agricultural practices, biomass energy can be considered sustainable. It is important to prioritize the use of waste materials, avoid deforestation, and ensure responsible land use practices.

Answer: Biomass can come from various sources:
Answer: Biomass energy differs from other renewable sources in terms of its fuel type. While solar and wind energy harness sunlight and wind, respectively, biomass energy relies on organic materials for combustion or conversion. Biomass can also offer continuous power generation, unlike solar or wind energy that depends on weather conditions.
Answer: Yes, biomass energy can be converted to biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, which can be used in transportation. Biofuels derived from biomass can act as substitutes for traditional petroleum-based fuels, reducing carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
Answer: Biomass energy has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. When sustainably sourced biomass materials are used and carbon emissions from combustion are offset through forest regrowth or other carbon sequestration measures, biomass can be considered a carbon-neutral or even a carbon-negative energy source.
Answer: Biomass energy production can provide economic opportunities and contribute to rural development. It can create jobs in biomass cultivation, harvesting, transportation, and processing. Additionally, decentralized biomass power plants can help in supplying electricity to remote areas, promoting economic growth and energy access in rural communities.
Answer: Many countries have implemented policies and incentives to encourage the use of biomass energy. These may include feed-in tariffs, tax credits, renewable energy subsidies, and renewable portfolio standards. Such incentives aim to promote the growth of the biomass energy sector and support the transition to a more sustainable energy mix.
Answer: Scaling up biomass energy production can face various challenges:
Answer: While biomass energy can contribute significantly to the energy mix and reduce dependence on fossil fuels, it is unlikely to completely replace them. Biomass energy alone may not be sufficient to meet the growing energy demand of industries and transportation. However, when integrated with other renewable sources like wind, solar, and hydropower, it can play a significant role in achieving a more sustainable and diversified energy system.
Overall, biomass energy offers both advantages and disadvantages. It is deemed renewable and can help reduce carbon emissions when sourced from sustainable materials. However, it also presents challenges related to emissions, land use, and logistics. With proper management and technological advancements, biomass energy can be a valuable component of the transition to a greener and more sustainable energy future.