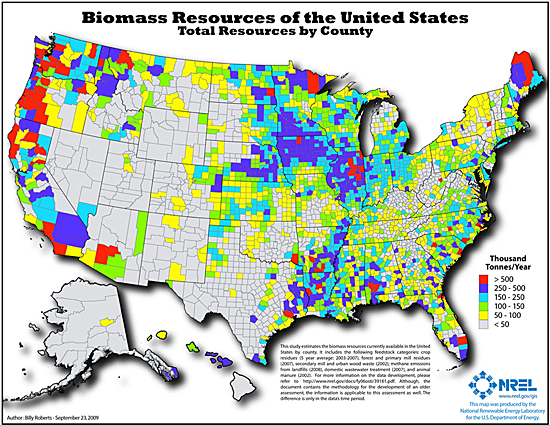
where is biomass energy used in the us
Biomass for Electricity Generation
Biomass is a renewable energy source that involves the use of organic materials, such as plants and animal waste, to generate electricity. It is a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels and plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions. In this article, we will explore the benefits, challenges, and applications of biomass for electricity generation.
Question 1: How does biomass generate electricity?
NLP Answer: Biomass generates electricity through a process called combustion. Organic materials, such as wood chips or agricultural waste, are burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam drives a turbine, which in turn generates electricity.
Expert Answer: Biomass power plants use different technologies to convert organic materials into electricity. The most common method is combustion, where biomass is burned to produce steam. This steam is used to rotate a turbine connected to a generator, which creates electricity. Other technologies include gasification, pyrolysis, and anaerobic digestion, which convert biomass into a gaseous, liquid, or biogas fuel that can be used to generate electricity.
Additional Information:
- Combustion is the most widely deployed biomass energy technology.
- Gasification converts biomass into a combustible gas called syngas.
- Pyrolysis uses high temperatures to break down biomass into bio-oil, biochar, and gases.
- Anaerobic digestion decomposes biomass in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas.
- Biomass power plants are often co-located with other industries that produce organic waste.
Question 2: What are the benefits of biomass for electricity generation?
NLP Answer: Biomass for electricity generation offers several benefits, including a renewable energy source, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, waste management solution, and economic opportunities.
Expert Answer: Biomass for electricity generation has numerous advantages:
- Renewable Energy Source: Biomass is derived from organic materials, which can be regrown and replenished, making it a sustainable and renewable resource.
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but this is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of the organic materials. As a result, biomass power generation can help reduce net greenhouse gas emissions.
- Waste Management Solution: Biomass power plants can utilize agricultural residues, forestry waste, and other organic materials that would otherwise go to landfills or be left to decompose, contributing to pollution. By converting these waste materials into electricity, biomass power plants provide an effective waste management solution.
- Economic Opportunities: Biomass power generation creates jobs in the construction and operation of power plants, as well as in the biomass supply chain. It stimulates local economies, particularly in rural areas where biomass resources are abundant.
Question 3: What are the challenges of biomass for electricity generation?
NLP Answer: Challenges of biomass for electricity generation include high upfront costs, potential emissions, reliance on a constant biomass supply, and competition for biomass resources.
Expert Answer: While biomass offers significant advantages, it also presents some challenges:
- High Upfront Costs: Establishing a biomass power plant can be capital-intensive due to the need for specialized equipment, such as boilers and turbines.
- Potential Emissions: Although biomass combustion can reduce net greenhouse gas emissions, it does release carbon dioxide and air pollutants, such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide. Proper emission controls and sustainable biomass sourcing are necessary to minimize these impacts.
- Reliance on Biomass Supply: Biomass power plants depend on a steady supply of organic materials, which may be affected by changes in agricultural practices, forestry management, or weather conditions. Ensuring a continuous and sustainable biomass supply can be challenging.
- Competition for Biomass Resources: There is competition for biomass resources among various sectors, including electricity generation, biofuels, and the production of bio-based products. Balancing these demands and preventing resource depletion is crucial.
Question 4: What are the main applications of biomass for electricity generation?
NLP Answer: Biomass is primarily used for electricity generation in power plants, but it can also be utilized for district heating, combined heat and power (CHP) systems, and cogeneration.
Expert Answer: Biomass has several applications in electricity generation:
- Power Plants: Biomass power plants produce electricity on a large scale, typically feeding it into the grid to meet the energy needs of homes, businesses, and industries.
- District Heating: Biomass can be burned to generate heat for district heating systems, where hot water or steam is distributed through a network of pipes to heat multiple buildings or a whole community.
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP): CHP systems, also known as cogeneration, use biomass to simultaneously generate both electricity and heat. The heat produced during electricity generation can be utilized for space heating, water heating, or industrial processes.
Question 5: How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources?
NLP Answer: Biomass has advantages and disadvantages compared to other renewable energy sources like wind, solar, and hydro power.
Expert Answer: Biomass offers certain advantages and disadvantages in comparison to other renewable energy sources:
- Advantages:
- Reliable Baseload Power: Biomass power plants can provide a consistent supply of electricity, regardless of weather conditions, making them more reliable than wind and solar power.
- Flexible Dispatch: Biomass power plants can be dispatched in response to varying electricity demand, enabling them to provide stable and continuous power to the grid.
- Decentralized Generation: Biomass resources are widely distributed, allowing for localized power generation and reduced transmission losses.
- Disadvantages:
- Emissions and Air Quality: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide and air pollutants, albeit at lower levels compared to fossil fuel power plants. Still, proper emission controls are necessary to minimize environmental impacts.
- Biomass Availability: The availability and sustainability of biomass resources vary across regions, and competition with other sectors can limit its accessibility.
- Land Use Impacts: Expanding biomass production may require dedicated land, potentially conflicting with other land uses such as agriculture, forestry, or natural habitats.
Question 6: Is biomass considered a clean energy source?
NLP Answer: Biomass is often considered a clean energy source due to its ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but it does emit carbon dioxide and air pollutants during combustion.
Expert Answer: Biomass can be considered a cleaner energy source compared to fossil fuels, as it has a lower carbon footprint and can contribute to reducing net greenhouse gas emissions. However, biomass combustion does release carbon dioxide and air pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur dioxide. Implementing emission controls, sustainable biomass sourcing, and utilizing advanced conversion technologies can enhance the environmental performance of biomass power plants.
Question 7: How sustainable is biomass for electricity generation?
NLP Answer: Biomass can be sustainable for electricity generation if sourced responsibly and managed effectively.
Expert Answer: The sustainability of biomass for electricity generation depends on several factors:
- Sustainable Sourcing: Biomass should be sourced from sustainably managed forests, agricultural practices, or organic waste streams. Proper sourcing and management can ensure the long-term availability of biomass resources.
- Land Use and Biodiversity: Biomass production should not result in the conversion of natural habitats or disrupt biodiversity. Balancing land use for biomass with other purposes, such as food production or nature conservation, is crucial.
- Emissions and Air Quality: Biomass power plants should employ emission control technologies to minimize the release of air pollutants and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
- Efficiency and Conversion Technologies: Using efficient biomass conversion technologies can maximize electricity generation from available biomass resources, reducing waste and improving resource efficiency.
Question 8: What role does biomass play in reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
NLP Answer: Biomass plays a significant role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions by offsetting carbon dioxide released during combustion with the carbon dioxide absorbed during plant growth.
Expert Answer: Biomass for electricity generation can contribute to reducing net greenhouse gas emissions. The carbon dioxide released when biomass is burned during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth. As long as biomass is sourced sustainably and the emissions from combustion are properly controlled, the net effect is a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. Biomass power plants can replace coal-fired power plants, which emit significantly higher levels of carbon dioxide, further reducing the overall carbon footprint of electricity generation.
Question 9: How can biomass address waste management challenges?
NLP Answer: Biomass power plants can contribute to waste management by utilizing agricultural residues, forestry waste, and other organic materials that would otherwise be left to decompose or go to landfills.
Expert Answer: Biomass power plants offer an effective waste management solution by utilizing various organic materials that would otherwise contribute to pollution. Agricultural residues, such as crop residues and animal waste, forestry waste, and other organic byproducts can be used as feedstock for biomass power generation. Converting these organic materials into electricity not only reduces greenhouse gas emissions but also reduces the burden on landfills and fosters a circular economy. For example, residues from the forestry industry, such as wood chips or sawdust, can be used to generate electricity instead of being discarded, thus reducing waste and maximizing resource utilization.
Question 10: What are the economic opportunities associated with biomass for electricity generation?
NLP Answer: Biomass for electricity generation offers economic opportunities through job creation and stimulation of local economies.
Expert Answer: Biomass power generation brings several economic opportunities:
- Job Creation: The construction, operation, and maintenance of biomass power plants require a skilled workforce, creating jobs in the renewable energy sector. Additionally, the biomass supply chain, including sourcing, transportation, and processing, generates employment opportunities.
- Local Economy Stimulation: Biomass power plants are often located in rural areas with abundant biomass resources. These plants stimulate local economies by providing a market for biomass feedstock, supporting local farmers, foresters, and suppliers. Revenue generated from electricity sales can be reinvested in the community, thereby driving economic growth.
- Energy Independence: Biomass power generation reduces reliance on imported fuels and enhances energy security by utilizing local biomass resources. This can result in cost savings and economic stability.
Question 11: Are there any subsidies or incentives available for biomass for electricity generation?
NLP Answer: Depending on the region, subsidies and incentives may be available to promote biomass for electricity generation.
Expert Answer: The availability of subsidies and incentives for biomass power generation depends on government policies and regional initiatives. Some of the support mechanisms that may be offered include:
- Feed-in Tariffs: Governments may provide feed-in tariffs, which guarantee a fixed payment for each unit of electricity generated from biomass, ensuring a stable return on investment for biomass power plant operators.
- Tax Credits and Grants: Tax credits or grants can be offered to biomass power plant developers or investors to encourage the deployment of renewable energy projects.
- Renewable Portfolio Standards: Governments can set renewable portfolio standards, requiring a certain percentage of electricity generation to come from renewable sources, including biomass. Compliance with these standards may result in financial incentives or exemptions.
- Renewable Energy Certificates: Biomass power plants may earn renewable energy certificates for each unit of electricity generated. These certificates can be sold to electricity retailers or other entities looking to offset their carbon footprint.
Question 12: What are some successful case studies of biomass for electricity generation?

NLP Answer: Successful biomass power generation case studies can be found worldwide, including countries such as the United States, Sweden, and Brazil.
Expert Answer: Here are a few successful case studies that highlight the potential of biomass for electricity generation:
- United States: The McNeil Generating Station in Burlington, Vermont, is one of the largest biomass power plants in the United States. It utilizes wood chips and other biomass materials to generate approximately 50 megawatts of electricity, contributing to the state's renewable energy targets and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
- Sweden: Sweden has a well-established biomass power sector and utilizes biomass from forests sustainably. The Stockholm Exergi Värtan biomass cogeneration plant, located in Stockholm, produces both heat and electricity by burning wood pellets. It plays a significant role in the city's district heating system, supplying heat to thousands of households and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Brazil: Brazil has been successful in utilizing sugarcane bagasse, a residue from the sugarcane industry, as a biomass feedstock for electricity generation. The bagasse is burned in boilers to produce steam, which powers turbines and generates electricity. This process is commonly used in sugarcane-producing regions, such as São Paulo, contributing to the country's renewable energy mix.
As biomass continues to evolve as a renewable energy source, advancements in technology, sustainable sourcing practices, and supportive policies will further enhance its role in electricity generation. By harnessing the power of biomass, we can move towards a more sustainable and greener energy future.