where can you find biomass energy
Pros and Cons of Renewable Energy You May Not Know About

Renewable energy is becoming increasingly popular due to its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. However, there are both pros and cons associated with renewable energy sources like biomass energy. In this article, we will explore the advantages and disadvantages of renewable energy.
1. What is biomass energy?
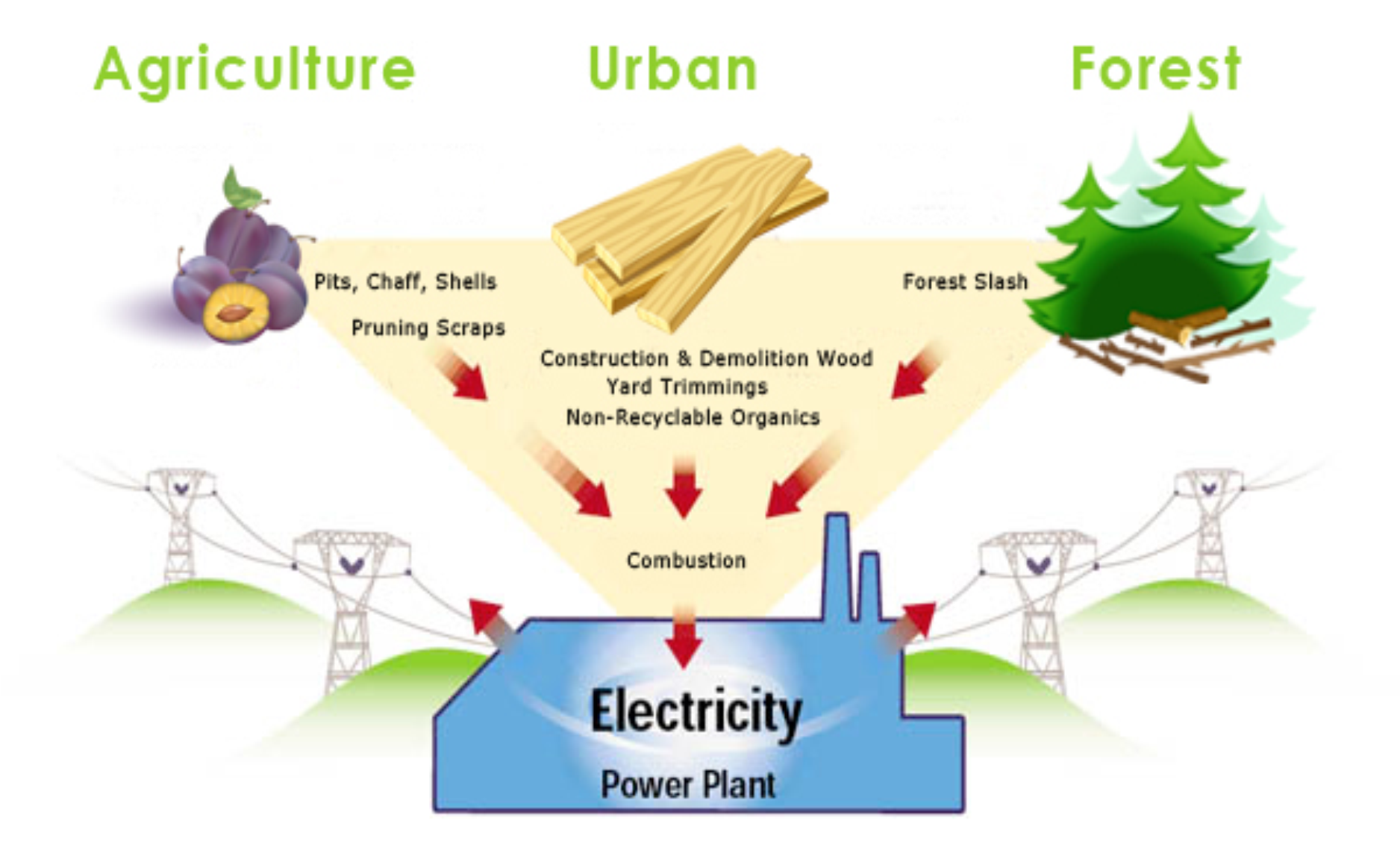
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as plants, crop residues, forestry products, and agricultural byproducts. These organic materials are used to produce heat, electricity, and fuel. Biomass is considered a renewable energy source because it can be regrown or replenished.
- Biomass can be sourced from various organic materials, including wood, crop residues, and animal manure.
- It is a renewable energy source as organic materials can be regrown or replenished.
- Biomass energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions by replacing fossil fuels.
- It provides opportunities for waste management by utilizing agricultural and forestry residues.
- Biomass energy can support rural economies by creating jobs in biomass production, processing, and transportation.
- It can contribute to energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels.
- Biomass energy systems can be integrated with traditional power plants to enhance overall efficiency.
2. What are the advantages of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several advantages over conventional forms of energy:
- Biomass is a sustainable and renewable energy source.
- It helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigates climate change.
- Biomass energy systems can be flexible and can utilize a variety of organic materials.
- It provides an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing dependence on finite resources.
- Biomass energy can be generated locally, promoting energy security and decentralization.
- It supports rural development and job creation in the biomass industry.
- Biomass energy can help dispose of organic waste in an environmentally friendly manner.
3. What are the disadvantages of biomass energy?
While biomass energy has many benefits, there are also some potential drawbacks:
- Large-scale biomass production may require significant land resources.
- Transporting biomass materials to energy plants can be costly and energy-intensive.
- Some types of biomass, such as wood pellets, are not as energy-dense as fossil fuels.
- Biomass energy systems may emit certain air pollutants, although improved technologies can reduce emissions.
- It may compete with food production if agricultural crops are used for biomass feedstock.
- Continuous and efficient supply of biomass feedstock can be a challenge.
4. How does biomass energy contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions?
Biomass energy can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions in several ways:
- During photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When burned as biomass, the carbon released is reabsorbed by new plant growth, resulting in a closed carbon cycle.
- Compared to coal or natural gas, biomass combustion produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide.
- By replacing fossil fuels with biomass energy, we can reduce the overall carbon footprint and mitigate climate change.
5. How does biomass energy help with waste management?
Biomass energy can contribute to effective waste management by utilizing agricultural and forestry residues that would otherwise be discarded. These organic materials can be converted into energy through various processes:
- Combustion: Biomass is burned to produce heat, which can be used for electricity generation or heating.
- Gasification: Biomass is heated in a low-oxygen environment to produce a synthetic gas, which can be used for power generation or converted into liquid fuels.
- Anaerobic digestion: Organic waste materials are decomposed by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used for heat or electricity.
6. Can biomass energy support rural economies?
Yes, biomass energy can provide economic opportunities for rural areas:
- Establishing biomass production and processing facilities can create jobs in agriculture, forestry, and transportation.
- Rural communities can benefit from the sale of biomass feedstock to energy plants.
- Biomass energy production can help diversify rural economies by offering an additional income source.
7. How does biomass energy contribute to energy independence?
By utilizing biomass energy sources, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels:
- Biomass resources are often locally available, reducing the need for long-distance fuel transportation.
- Developing biomass energy infrastructure allows countries to utilize their own renewable resources for energy production.
- Reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports enhances energy security and can stabilize energy prices.
8. Can biomass energy be integrated into existing power plants?
Yes, biomass energy systems can be integrated with traditional power plants to enhance overall efficiency and reduce emissions:
- Biomass can be co-fired with coal in existing coal-fired power plants.
- Converting coal plants to biomass power plants can reduce carbon emissions and environmental impact.
- Combined heat and power (CHP) systems can utilize biomass energy for both electricity and heat generation, increasing energy efficiency.
9. How is biomass energy different from other renewable energy sources?
Biomass energy is unique compared to other renewable energy sources:
- Unlike solar or wind energy, biomass can be stored and used on-demand, providing a more consistent power supply.
- Biomass energy can be generated using various organic materials, making it versatile and adaptable to different regions and industries.
- While solar and wind energy are intermittent, biomass energy can produce continuous power, making it suitable for baseload electricity generation.
10. Can biomass energy be used for transportation?
Yes, biomass energy can be converted into liquid fuels, such as biofuels, which can be used for transportation purposes:
- Biofuels, such as biodiesel and ethanol, can be produced from biomass feedstock and blended with conventional fuels.
- Biofuels help reduce greenhouse gas emissions from the transportation sector and promote sustainability.
- With advancements in biofuel production technologies, biomass can play a significant role in decarbonizing the transportation sector.
11. Are there any government incentives for biomass energy?
Many governments provide incentives and support for biomass energy development:
- Feed-in tariffs: Governments offer a guaranteed price for electricity generated from biomass, ensuring stable and attractive returns for investors.
- Tax incentives: Tax credits or exemptions may be provided for biomass energy project developers or biomass feedstock suppliers.
- Grants and subsidies: Governments provide financial assistance for the establishment of biomass energy plants or research and development activities.
12. What is the future outlook for biomass energy?
The future of biomass energy looks promising, with several ongoing developments and opportunities:
- Advancements in biomass conversion technologies are making it more efficient and cost-effective.
- Increased focus on reducing carbon emissions and transitioning to renewable energy sources will drive the demand for biomass energy.
- Integration of biomass with other renewable energy systems, such as solar and wind, can create a more sustainable and reliable energy mix.
- Research is underway to explore the use of algae and waste-to-energy technologies for biomass energy production.