what is the most common way to release biomass energy
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice - REURASIA
In recent years, the importance of renewable energy sources has become increasingly evident. Biomass energy, in particular, has gained attention as a viable and sustainable option for meeting our energy needs. This article discusses the reasons why biomass energy should be considered as a top choice for powering our future.
1. What is biomass energy?
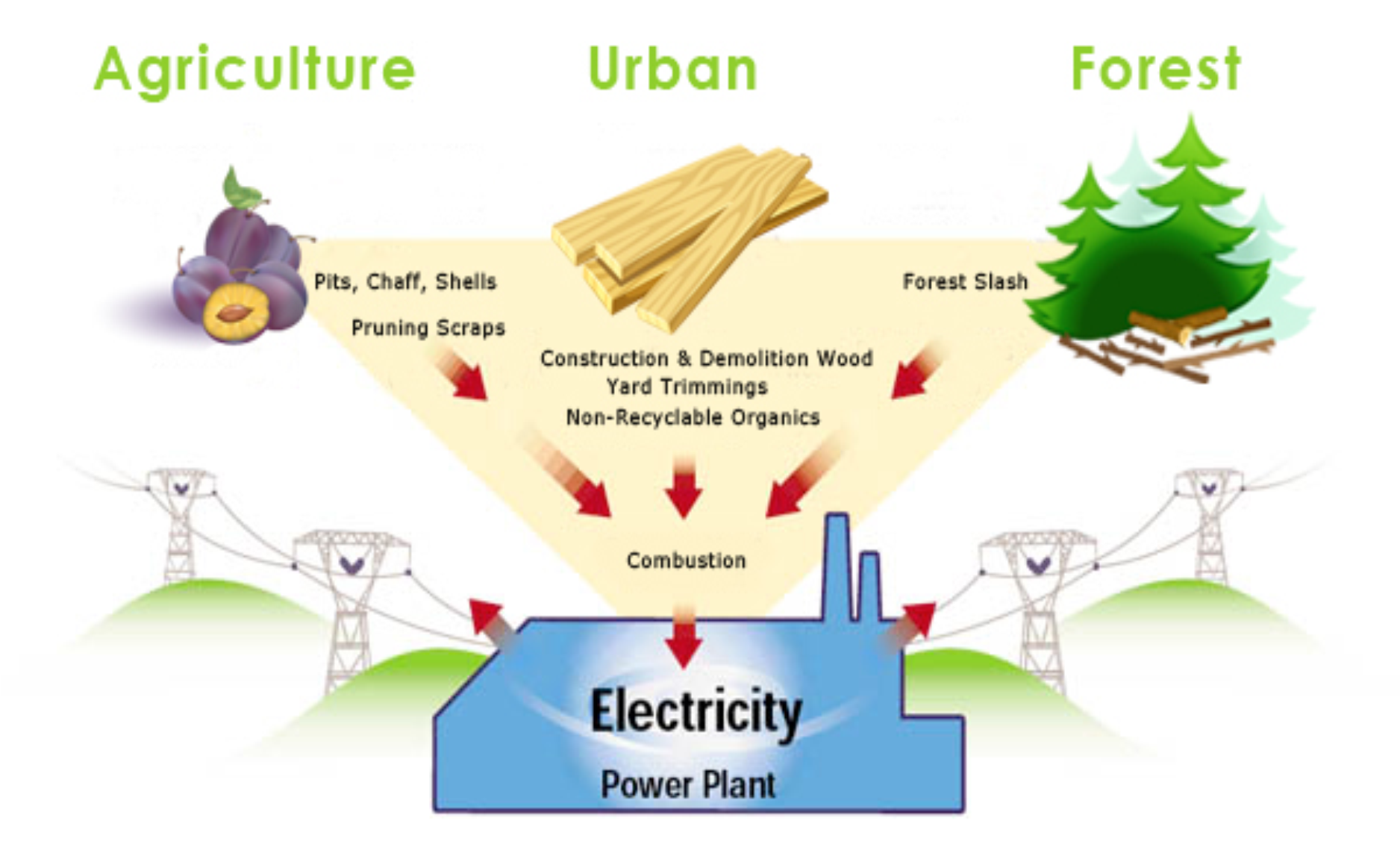
Biomass energy refers to the energy produced from organic materials such as plants, agricultural waste, and wood residues. These materials are converted into usable energy through various processes like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
Key points:
- Biomass energy is derived from organic materials.
- It can be generated through processes like combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
- Biomass energy is considered a renewable energy source.
2. How is biomass energy different from fossil fuels?

Biomass energy differs from fossil fuels primarily in terms of their origins. Fossil fuels are formed from ancient organic matter over millions of years and are finite in supply. On the other hand, biomass energy relies on recently living organic matter, which is renewable and abundant.
Key points:
- Biomass energy comes from recently living organic matter.
- Fossil fuels are derived from ancient organic matter and are finite.
- Biomass energy is considered a renewable energy source, while fossil fuels are non-renewable.
3. What are the benefits of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers numerous benefits that make it an attractive option:
- Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is a renewable energy source that can be sustainably produced and continually replenished.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy has lower carbon dioxide emissions compared to fossil fuels, contributing to mitigating climate change.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: Biomass energy diversifies our energy sources and reduces dependence on finite fossil fuels.
- Utilization of agricultural waste: Biomass energy can make use of agricultural residue and waste, providing an additional income stream for farmers.
- Potential for rural development: Biomass energy projects can promote rural economic development through job creation and investment opportunities.
4. How is biomass energy generated?
Biomass energy can be generated through different processes:
- Combustion: Biomass materials are burned directly to produce heat, which can then be used for various purposes such as electricity generation or heating.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a mixture of gases, including carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane, that can be used for electricity generation and other applications.
- Anaerobic digestion: Biomass is broken down by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas that can be used for electricity and heat production.
Key points:
- Biomass energy can be generated through combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion processes.
- The chosen method depends on the type of biomass and the desired end-use of the energy.
5. What are the challenges of implementing biomass energy?
While biomass energy offers many benefits, there are also challenges associated with its implementation:
- Resource availability: Biomass availability and quality can vary, making it necessary to ensure a stable and sustainable supply chain.
- Emission control: Certain biomass combustion processes may produce emissions that need to be properly managed to minimize environmental impacts.
- Land and water requirements: Large-scale biomass energy production may require significant amounts of land and water resources, which can pose challenges in areas with limited availability.
- Competition with food production: The use of biomass for energy production can potentially compete with food production, highlighting the importance of sustainable biomass sourcing.
6. Is biomass energy economically viable?
The economic viability of biomass energy projects depends on various factors:
- Scale of operations: Larger-scale biomass energy projects tend to have better economies of scale and cost-effectiveness.
- Feedstock availability: The availability and cost of biomass feedstock play a crucial role in the economic viability of biomass energy projects.
- Government policies and incentives: Supportive policies and incentives, such as feed-in tariffs and tax credits, can significantly impact the economic feasibility of biomass energy.
- Technological advancements: Advances in biomass conversion technologies can improve efficiency and reduce costs, enhancing the economic viability of biomass energy.
7. Can biomass energy help reduce carbon emissions?
Biomass energy has the potential to contribute to reducing carbon emissions in several ways:
- Carbon neutrality: Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during the growth of biomass feedstock.
- Replacing fossil fuels: Biomass energy can substitute for fossil fuels in various sectors, leading to lower carbon emissions.
- Waste-to-energy conversion: Biomass energy allows for the utilization of organic waste materials that would otherwise decompose and emit methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
8. Can biomass energy be used in transportation?
Yes, biomass energy can be used in transportation through various means:
- Biofuels: Biomass can be converted into liquid biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, which can be used as a substitute for gasoline and diesel fuels.
- Biogas: Biomass can be converted into biogas, which can fuel vehicles when compressed or liquefied.
- Hydrothermal processes: Biomass can undergo hydrothermal conversion to produce renewable hydrocarbons, which can be used as transportation fuels.
9. Is biomass energy expensive to produce?
The cost of producing biomass energy can vary depending on several factors:
- Feedstock availability: The availability and cost of biomass feedstock play a significant role in overall production costs.
- Conversion technology: The choice of biomass conversion technology and its efficiency can impact the cost-effectiveness of biomass energy.
- Economies of scale: Larger-scale biomass energy projects tend to have better economies of scale, leading to lower production costs.
10. How does biomass energy contribute to rural development?
Biomass energy projects can contribute to rural development in multiple ways:
- Job creation: Establishing biomass energy facilities can create employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Income generation: Biomass energy production can provide additional income streams for farmers through the sale of biomass feedstock.
- Local investment: Biomass energy projects often attract investments, leading to economic growth and development in rural communities.
- Energy independence: Biomass energy reduces dependency on external energy sources, providing rural communities with a sense of energy independence.
11. How can biomass energy be integrated into existing energy systems?
Integrating biomass energy into existing energy systems requires careful planning and consideration:
- Grid integration: Biomass energy can be integrated into the electrical grid, allowing for seamless integration and distribution of the generated electricity.
- Co-firing: Biomass can be co-fired with fossil fuels in existing power plants, reducing the overall carbon emissions and utilizing existing infrastructure.
- Combined heat and power (CHP): Biomass energy can be used for combined heat and power applications, providing both electricity and heat to industries and communities.
- Energy storage: Pairing biomass energy with energy storage technologies can help balance the intermittent nature of biomass energy generation.
12. What are some successful case studies of biomass energy implementation?
Several successful case studies showcase the effective implementation of biomass energy:
- European Union: The EU has been a pioneer in biomass energy utilization, with several countries adopting biomass for electricity and heat production.
- Denmark: Denmark has successfully integrated biomass into its energy system, utilizing biomass for combined heat and power generation.
- United States: Many U.S. states, such as California and Oregon, have implemented biomass projects, providing renewable energy and supporting local economies.
- India: India has shown significant progress in utilizing biomass for electricity generation, contributing to rural development and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
Overall, biomass energy presents a promising alternative to fossil fuels, offering sustainability, reduced carbon emissions, and potential benefits for rural communities. With continued advancements in technology and supportive policies, biomass energy can play a significant role in our transition towards a greener and more sustainable future.