what is the cost of biomass energy
Article: The Cost and Benefits of Biomass Power
1. What is biomass power?
Biomass power refers to the generation of electricity or heat from organic materials such as plants, wood, agricultural residues, or waste. It involves the combustion or gasification of biomass to produce energy.
Benefits of Biomass Power:
- Renewable Energy Source: Biomass is derived from plants and waste materials, making it a sustainable and renewable energy source.
- Reduces Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass power produces less greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping to mitigate climate change.
- Waste Management: Biomass power utilizes agricultural residues and waste materials, helping to reduce the burden on landfills and promoting efficient waste management.
2. How much does biomass power cost?
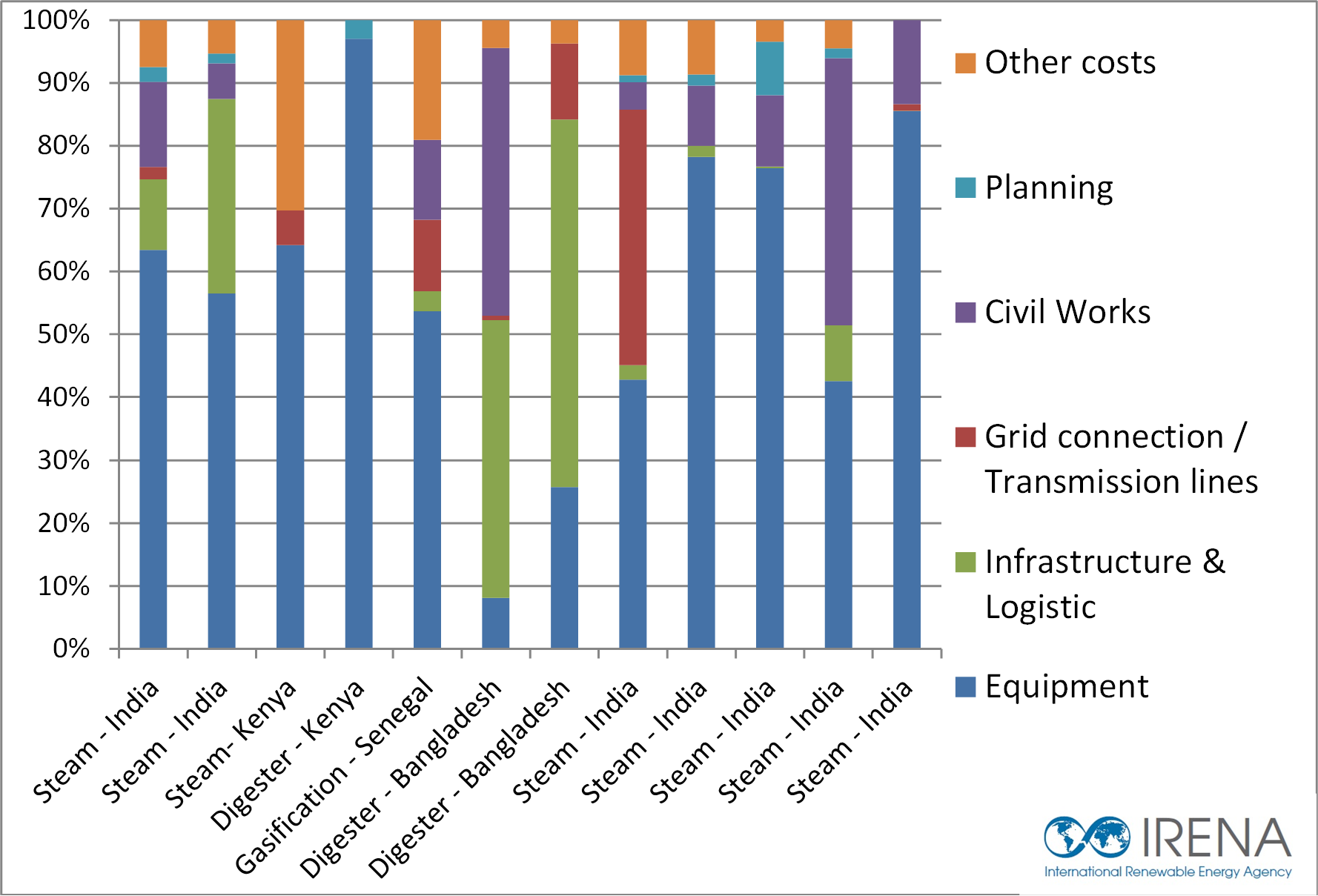
The cost of biomass power can vary depending on various factors such as the scale of the project, biomass feedstock availability, technology used, and local market conditions. Generally, biomass power plants require higher upfront investment compared to conventional fossil fuel-based power plants.
Factors influencing biomass power costs:
- Feedstock Costs: The availability and cost of biomass feedstock play a significant role in biomass power economics. Access to affordable and sustainable biomass sources is crucial.
- Technology Efficiency: The efficiency of biomass conversion technologies affects the cost of power generation. Advanced technologies like gasification and combined heat and power (CHP) systems can improve efficiency and reduce costs.
- Operational and Maintenance Costs: Regular maintenance and operational costs impact the overall economics of biomass power plants. Factors like labor, fuel transportation, and ash disposal contribute to the operating costs.
3. What are the environmental benefits of biomass power?
Biomass power has several environmental benefits:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO2), but since the plants used for biomass growth absorb CO2 during their lifecycle, the process is considered carbon-neutral. This helps reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions.
- Improved Air Quality: Biomass combustion emits fewer harmful pollutants than fossil fuels, resulting in improved air quality and reduced health risks.
- Promotes Sustainable Land Use: Biomass feedstock can be sourced from sustainable forestry practices, agricultural residues, or waste materials, preventing deforestation and promoting responsible land use.
4. What are the challenges of biomass power?
While biomass power has numerous benefits, it also faces certain challenges:
- Feedstock Availability: Ensuring a reliable, sustainable, and affordable supply of biomass feedstock can be challenging, especially on a large scale. Competition for biomass resources can also drive up costs.
- Technology Limitations: Some biomass conversion technologies are still in the early stages of development and may not be commercially viable or cost-effective.
- Emissions Reduction: While biomass power reduces greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, certain emissions such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) still need to be managed to minimize environmental impacts.
5. How does biomass power contribute to the renewable energy mix?
Biomass power plays a significant role in diversifying the renewable energy mix. It provides a reliable and dispatchable renewable energy source that can complement intermittent sources like wind and solar power.
Benefits of biomass power in the renewable energy mix:
- Base Load Power Generation: Biomass power plants can operate continuously and provide a stable base load of electricity, ensuring grid stability and reliability.
- Seasonal Energy Availability: Biomass feedstock can be stored and utilized during periods of high electricity demand, such as winter, when solar and wind power generation may be limited.
- Flexible Fuel Sources: Biomass power plants can use a variety of feedstock sources, ensuring energy production even during times of scarcity or changing biomass availability.
6. How does biomass power compare to other renewable energy sources?
While each renewable energy source has its own advantages and limitations, biomass power offers unique benefits:
- Dispatchable and Flexible: Biomass power plants can ramp up or down their electricity production based on demand, providing flexibility to support grid stability.
- Seasonal Availability: Unlike solar or wind power, biomass power can operate year-round, providing consistent electricity supply throughout the seasons.
- Waste Utilization: Biomass power efficiently utilizes agricultural residues and waste materials, reducing the burden on landfills and offering a sustainable waste management solution.
7. Are there any negative environmental impacts of biomass power?
While biomass power has significant environmental benefits, it can also have some negative impacts:
- Land Use: Biomass production requires land resources, which can lead to habitat loss and competition with food crops. Sustainable land use practices and responsible sourcing are necessary to mitigate these impacts.
- Emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide (CO2), as well as other emissions such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Proper emission controls and monitoring are essential to minimize environmental impacts.
- Transportation: Transporting biomass feedstock over long distances can result in carbon emissions from transportation vehicles. Locally available feedstock can help reduce transportation-related emissions.
8. How does biomass power contribute to rural development?
Biomass power has the potential to contribute to rural development in several ways:
- Job Creation: Biomass power projects require skilled and unskilled labor for operations, maintenance, and feedstock supply. This can create employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Local Economy: Biomass power plants can stimulate the local economy by contributing to the demand for biomass feedstock, supporting local agriculture, and attracting investment in the region.
- Energy Independence: Biomass power production in rural areas can help reduce dependence on external energy sources, providing energy security and resilience for local communities.
9. What role does government policy play in promoting biomass power?
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the development and utilization of biomass power:
- Renewable Energy Targets: Governments set renewable energy targets to encourage the adoption of sustainable energy sources, including biomass power.
- Feed-in Tariffs: Feed-in tariffs provide a guaranteed price for the electricity generated from biomass power plants. This helps attract investment and ensures a favorable economic outlook for biomass projects.
- Tax Incentives: Governments may offer tax incentives, grants, or subsidies to support the development and operation of biomass power plants, making them more economically viable.
10. Can biomass power be combined with other energy generation technologies?
Yes, biomass power can be combined with other energy generation technologies to create hybrid systems:
- Combined Heat and Power (CHP): Biomass power plants can be integrated with CHP systems to utilize the waste heat generated during electricity production. This co-generation improves overall energy efficiency.
- Gasification: Biomass gasification technology can produce synthesis gas (syngas), which can be further used in combined cycle gas turbines for electricity generation, improving overall system efficiency.
- Solar-Biomass Hybrid: Solar and biomass power can be integrated to provide a stable and dispatchable renewable energy mix, utilizing both the constant availability of biomass and intermittent solar power generation.
11. What is the future outlook for biomass power?
The future outlook for biomass power is promising, driven by the need to transition to cleaner and more sustainable energy sources. Some key trends for the future include:
- Technology Advancements: Continued research and development in biomass conversion technologies will improve efficiency, reduce costs, and expand the range of biomass feedstocks that can be utilized.
- Integrated Systems: Integration of biomass power with other renewable energy sources, storage technologies, and smart grid systems will enhance grid stability and optimize renewable energy utilization.
- Sustainable Practices: Adoption of sustainable land use practices, responsible sourcing of biomass feedstock, and stringent emission controls will ensure the environmental sustainability of biomass power.
12. Are there any notable biomass power projects or success stories?
Yes, there are several notable biomass power projects and success stories:
- Nordjylland Power Station, Denmark: One of the largest biomass power plants in the world, it utilizes wood pellets and agricultural residues to generate electricity and district heating.
- Drax Power Station, United Kingdom: Drax has transformed itself from a coal-fired power station to a predominantly biomass power plant, significantly reducing carbon emissions.
- Bioenergy Villages, Austria: Numerous rural communities in Austria have created self-sustaining energy systems by utilizing local biomass resources for heat and power generation.