what is the main source of biomass energy
Agustus 26, 2024
Dipublikasikan
Maret 14, 2023
Reasons Why Biomass Energy Should Be a Top Choice
1. What is biomass energy and how does it work?
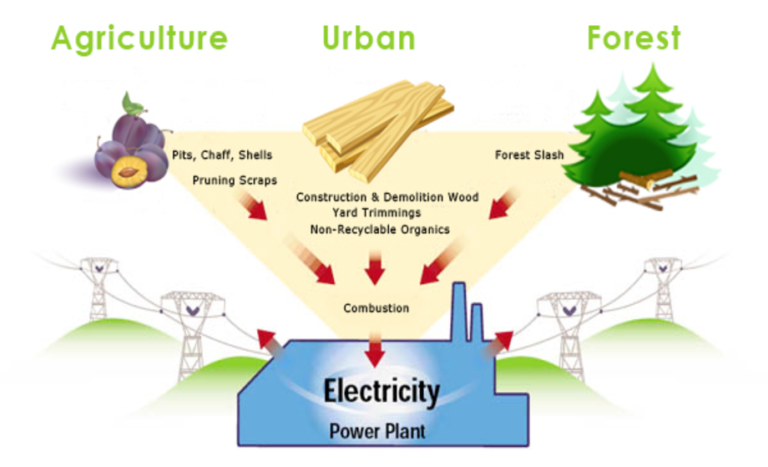 Biomass energy refers to the use of organic material, such as plants, wood, and agricultural residues, to generate heat, electricity, or fuel. This renewable energy source works by burning biomass to release energy in the form of heat, which can then be converted into various forms of usable energy. Comprehensive structured answer: Biomass energy utilizes organic matter to produce heat, electricity, or fuel. It involves the combustion of biomass, which releases energy in the form of heat. This heat energy can be used directly or converted into electricity through steam turbines. Biomass can also be converted into biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel. Some key points related to biomass energy include: - Biomass is a renewable energy source as plants and organic waste are constantly replenished. - Using biomass energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based energy sources. - It provides an alternative to conventional energy sources, contributing to energy diversification and reducing reliance on finite resources.
Biomass energy refers to the use of organic material, such as plants, wood, and agricultural residues, to generate heat, electricity, or fuel. This renewable energy source works by burning biomass to release energy in the form of heat, which can then be converted into various forms of usable energy. Comprehensive structured answer: Biomass energy utilizes organic matter to produce heat, electricity, or fuel. It involves the combustion of biomass, which releases energy in the form of heat. This heat energy can be used directly or converted into electricity through steam turbines. Biomass can also be converted into biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel. Some key points related to biomass energy include: - Biomass is a renewable energy source as plants and organic waste are constantly replenished. - Using biomass energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuel-based energy sources. - It provides an alternative to conventional energy sources, contributing to energy diversification and reducing reliance on finite resources. 2. What are the benefits of biomass energy?
 Benefits of biomass energy include: - Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is constantly being generated, making it a renewable and sustainable energy source. - Reduced carbon emissions: Biomass energy releases carbon dioxide, but the plants used for biomass absorb an equal amount of carbon dioxide, resulting in a net zero carbon footprint. - Waste utilization: Biomass energy can be generated from agricultural waste, wood residues, and other organic materials, providing an environmentally friendly way to repurpose waste. - Local economic development: Biomass energy projects can create jobs and support local economies, particularly in rural areas with abundant biomass resources.
Benefits of biomass energy include: - Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is constantly being generated, making it a renewable and sustainable energy source. - Reduced carbon emissions: Biomass energy releases carbon dioxide, but the plants used for biomass absorb an equal amount of carbon dioxide, resulting in a net zero carbon footprint. - Waste utilization: Biomass energy can be generated from agricultural waste, wood residues, and other organic materials, providing an environmentally friendly way to repurpose waste. - Local economic development: Biomass energy projects can create jobs and support local economies, particularly in rural areas with abundant biomass resources. 3. How does biomass energy contribute to reducing environmental impact?
Biomass energy offers several environmental benefits: - Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but because the plants used for biomass absorb an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide during their growth, it results in a net zero carbon emission. - Reduced air pollution: When compared to fossil fuel combustion, biomass energy generally produces lower levels of air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. - Waste diversion: Biomass energy allows for the productive use of agricultural waste and wood residues that would otherwise contribute to landfill waste or be burned in an uncontrolled manner, causing air pollution. - Sustainable land management: Growing biomass feedstock can help improve soil quality, prevent soil erosion, and promote reforestation efforts, contributing to sustainable land management.
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but because the plants used for biomass absorb an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide during their growth, it results in a net zero carbon emission. - Reduced air pollution: When compared to fossil fuel combustion, biomass energy generally produces lower levels of air pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. - Waste diversion: Biomass energy allows for the productive use of agricultural waste and wood residues that would otherwise contribute to landfill waste or be burned in an uncontrolled manner, causing air pollution. - Sustainable land management: Growing biomass feedstock can help improve soil quality, prevent soil erosion, and promote reforestation efforts, contributing to sustainable land management. 4. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy?
Challenges related to biomass energy include: - Fuel availability and logistics: Ensuring a continuous supply of biomass feedstock in sufficient quantities can be challenging, especially in regions with limited biomass resources or poor infrastructure for its transportation. - Impact on food production: Biomass energy production competes with food production for land and resources. It is essential to strike a balance between biomass energy production and food security. - Efficiency and technology limitations: Biomass energy conversion technologies need further development to maximize energy efficiency and address potential environmental concerns associated with combustion. - Cost competitiveness: Biomass energy may face cost competitiveness challenges compared to conventional energy sources, particularly in regions with low-cost fossil fuels and established energy infrastructure.
- Fuel availability and logistics: Ensuring a continuous supply of biomass feedstock in sufficient quantities can be challenging, especially in regions with limited biomass resources or poor infrastructure for its transportation. - Impact on food production: Biomass energy production competes with food production for land and resources. It is essential to strike a balance between biomass energy production and food security. - Efficiency and technology limitations: Biomass energy conversion technologies need further development to maximize energy efficiency and address potential environmental concerns associated with combustion. - Cost competitiveness: Biomass energy may face cost competitiveness challenges compared to conventional energy sources, particularly in regions with low-cost fossil fuels and established energy infrastructure. 5. Which countries are interested in biomass energy?
6. What are the potential applications of biomass energy?
Biomass energy can be used in various applications, including: - Heat generation: Biomass can be burned to produce heat for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes, replacing traditional fossil fuel-based heating systems. - Electricity generation: Biomass can be combusted to generate electricity through steam turbines, similar to how coal-fired power plants operate. - Transportation fuels: Biomass can be processed into biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, which can be used as alternatives to gasoline and diesel fuels in vehicles.
- Heat generation: Biomass can be burned to produce heat for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes, replacing traditional fossil fuel-based heating systems. - Electricity generation: Biomass can be combusted to generate electricity through steam turbines, similar to how coal-fired power plants operate. - Transportation fuels: Biomass can be processed into biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel, which can be used as alternatives to gasoline and diesel fuels in vehicles. 7. Is biomass energy a reliable source of energy?
Biomass energy can be considered a reliable source of energy under certain conditions. Factors that contribute to its reliability include: - Availability of biomass feedstock: Biomass energy relies on a regular supply of organic materials. This requires proper planning, management, and access to a consistent feedstock source. - Adequate infrastructure: Biomass energy systems require appropriate infrastructure for collection, transportation, and storage of biomass feedstock. Investment in infrastructure is crucial to ensure a reliable supply chain. - Technology advancements: Continuous improvements in biomass energy conversion technologies enhance overall efficiency and reliability. - Energy storage solutions: Integrating energy storage technologies with biomass energy systems can help overcome variations in biomass availability and ensure a more reliable energy output.
- Availability of biomass feedstock: Biomass energy relies on a regular supply of organic materials. This requires proper planning, management, and access to a consistent feedstock source. - Adequate infrastructure: Biomass energy systems require appropriate infrastructure for collection, transportation, and storage of biomass feedstock. Investment in infrastructure is crucial to ensure a reliable supply chain. - Technology advancements: Continuous improvements in biomass energy conversion technologies enhance overall efficiency and reliability. - Energy storage solutions: Integrating energy storage technologies with biomass energy systems can help overcome variations in biomass availability and ensure a more reliable energy output. 8. Can biomass energy contribute to reducing reliance on fossil fuels?
 Yes, biomass energy can play a significant role in reducing dependence on fossil fuels. By utilizing organic materials, biomass energy offers a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based energy sources. It can help diversify the energy mix, reduce carbon emissions, and promote energy independence. However, it is important to note that a transition to a low-carbon and sustainable energy system requires a combination of various renewable energy sources, energy efficiency measures, and advancements in energy storage technologies.
Yes, biomass energy can play a significant role in reducing dependence on fossil fuels. By utilizing organic materials, biomass energy offers a renewable and sustainable alternative to fossil fuel-based energy sources. It can help diversify the energy mix, reduce carbon emissions, and promote energy independence. However, it is important to note that a transition to a low-carbon and sustainable energy system requires a combination of various renewable energy sources, energy efficiency measures, and advancements in energy storage technologies. 9. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources?
When compared to other renewable energy sources, biomass energy has its unique advantages and considerations: - Unlike solar and wind energy, biomass energy can provide baseload power due to its ability to store and release energy as required. - Biomass energy can make productive use of waste materials and provide a solution for waste management. - However, biomass energy may have higher upfront costs and environmental considerations compared to non-combustion-based renewables like solar and wind energy. - The choice of renewable energy sources should be based on a comprehensive assessment of local resource availability, environmental impact, and economic feasibility.
- Unlike solar and wind energy, biomass energy can provide baseload power due to its ability to store and release energy as required. - Biomass energy can make productive use of waste materials and provide a solution for waste management. - However, biomass energy may have higher upfront costs and environmental considerations compared to non-combustion-based renewables like solar and wind energy. - The choice of renewable energy sources should be based on a comprehensive assessment of local resource availability, environmental impact, and economic feasibility. 10. What role does policy play in promoting biomass energy?
Policy plays a crucial role in promoting biomass energy adoption and development: - Feed-in tariffs and renewable energy incentives: Governments can establish supportive policies such as feed-in tariffs and financial incentives that encourage biomass energy project development and ensure favorable market conditions. - Renewable energy targets: Setting renewable energy targets helps drive investments and create a market demand for biomass energy. These targets provide a clear direction and enable long-term planning. - Regulations and sustainability criteria: Governments can implement regulations to ensure sustainable biomass sourcing, address air quality concerns, and promote the responsible use of biomass resources. - Research and development funding: Governments can allocate funding for research and development initiatives to drive technological advancements in biomass energy and overcome technical hurdles.
- Feed-in tariffs and renewable energy incentives: Governments can establish supportive policies such as feed-in tariffs and financial incentives that encourage biomass energy project development and ensure favorable market conditions. - Renewable energy targets: Setting renewable energy targets helps drive investments and create a market demand for biomass energy. These targets provide a clear direction and enable long-term planning. - Regulations and sustainability criteria: Governments can implement regulations to ensure sustainable biomass sourcing, address air quality concerns, and promote the responsible use of biomass resources. - Research and development funding: Governments can allocate funding for research and development initiatives to drive technological advancements in biomass energy and overcome technical hurdles. 11. Are there any successful case studies of biomass energy implementation?
There are numerous successful case studies of biomass energy implementation worldwide: - Denmark: Denmark has achieved remarkable success in biomass energy utilization. It has developed district heating systems that rely on biomass for heat generation, reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy efficiency. - Sweden: Sweden is a global leader in utilizing biomass for combined heat and power generation. The country has established efficient biomass energy systems and achieved high levels of renewable energy integration. - United States: The United States has implemented biomass energy projects in various states, contributing to renewable energy targets. Biomass power plants and biofuel production facilities have been successfully established, utilizing a range of biomass feedstocks. These case studies highlight the feasibility and benefits of biomass energy across different geographical regions and serve as valuable examples for other countries considering biomass energy implementation.
- Denmark: Denmark has achieved remarkable success in biomass energy utilization. It has developed district heating systems that rely on biomass for heat generation, reducing carbon emissions and enhancing energy efficiency. - Sweden: Sweden is a global leader in utilizing biomass for combined heat and power generation. The country has established efficient biomass energy systems and achieved high levels of renewable energy integration. - United States: The United States has implemented biomass energy projects in various states, contributing to renewable energy targets. Biomass power plants and biofuel production facilities have been successfully established, utilizing a range of biomass feedstocks. These case studies highlight the feasibility and benefits of biomass energy across different geographical regions and serve as valuable examples for other countries considering biomass energy implementation. 12. What are the future prospects for biomass energy?
The future prospects for biomass energy are promising: - Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance biomass energy conversion technologies, improving efficiency, reducing emissions, and expanding feedstock options. - Integrated energy systems: Biomass energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to create hybrid systems that provide a reliable and continuous energy supply. - Carbon capture and utilization: Biomass energy combined with carbon capture and utilization techniques can offer carbon-negative solutions by actively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. - Sustainable biomass sourcing: Ensuring sustainable biomass sourcing practices, including reforestation, responsible land use, and efficient feedstock management, will be essential for long-term viability. - International collaborations: Collaborative efforts between countries can accelerate knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and policy development, fostering the global growth of biomass energy. Overall, biomass energy presents a significant opportunity for sustainable energy development, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and economic growth. Through continued advancements and support, biomass energy can further contribute to a cleaner and more resilient energy future.
- Technological advancements: Ongoing research and development efforts aim to enhance biomass energy conversion technologies, improving efficiency, reducing emissions, and expanding feedstock options. - Integrated energy systems: Biomass energy can be integrated with other renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, to create hybrid systems that provide a reliable and continuous energy supply. - Carbon capture and utilization: Biomass energy combined with carbon capture and utilization techniques can offer carbon-negative solutions by actively removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. - Sustainable biomass sourcing: Ensuring sustainable biomass sourcing practices, including reforestation, responsible land use, and efficient feedstock management, will be essential for long-term viability. - International collaborations: Collaborative efforts between countries can accelerate knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and policy development, fostering the global growth of biomass energy. Overall, biomass energy presents a significant opportunity for sustainable energy development, reduced greenhouse gas emissions, and economic growth. Through continued advancements and support, biomass energy can further contribute to a cleaner and more resilient energy future.